-

Proteins
Proteins are crucial biomolecules that perform a vast range of functions in living organisms, from providing mechanical support to catalyzing chemical reactions and protecting against pathogens. Composed of amino acids linked by peptide bonds, proteins come in various types, each with specific roles and characteristics. Structural proteins, such as collagen and elastin, provide support and…
-

Carbohydrates
The text provides an overview of carbohydrates, which are a class of biomolecules composed of simple sugars linked together through glycosidic bonds. Carbohydrates play crucial roles in energy storage and transport, as well as in structural support and cell-cell recognition. The three main types of carbohydrates are monosaccharides, disaccharides, and polysaccharides, each with specific functions…
-
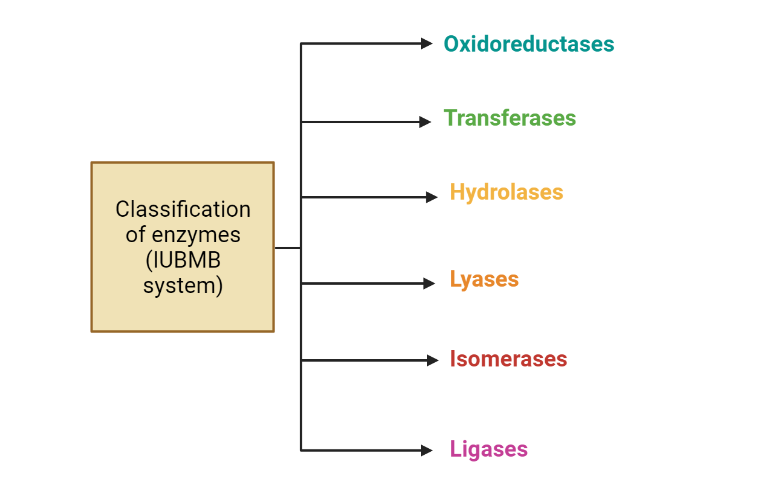
Enzymes : classification
Enzymes are incredibly important biomolecules that play a crucial role in the proper functioning of living organisms. They catalyze specific chemical reactions, making it possible for various biological processes such as metabolism, DNA replication, and cell signaling to occur efficiently. The structure of enzymes is complex, with different levels of organization, including the primary, secondary,…
-
Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR)
The Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) technique is a powerful tool used in biophysics to study the structure, dynamics, and interactions of biomolecules in solution. NMR spectroscopy is based on the principle that certain atoms’ nuclei can absorb and emit electromagnetic radiation in the radiofrequency range when placed in a strong magnetic field. This technique can…
-
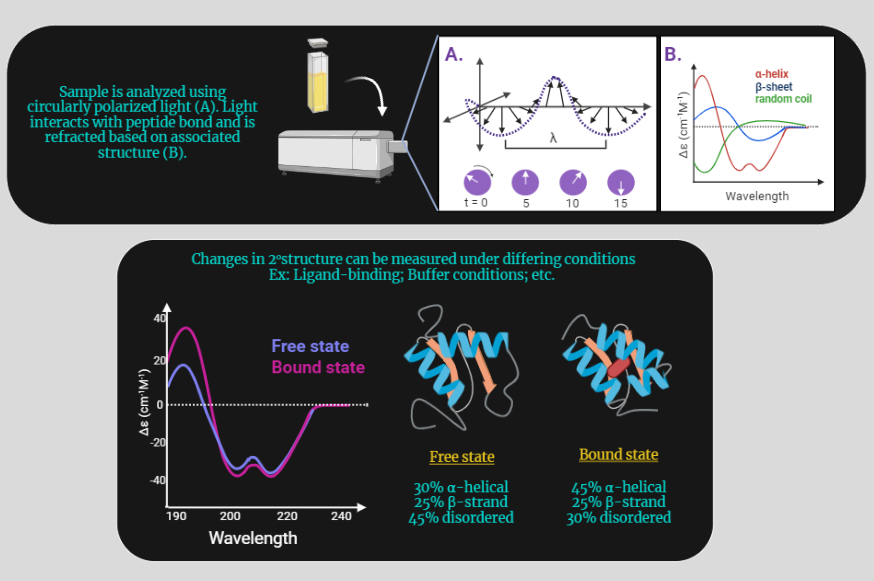
Circular Dichroism (CD) Technique
Circular dichroism (CD) is a powerful spectroscopic technique used to study the structure and properties of chiral molecules, such as proteins, nucleic acids, and carbohydrates. It is based on the differential absorption of left and right circularly polarized light by chiral molecules, which can provide information on their secondary, tertiary, and quaternary structures. In this…
Categories
- Anatomy (9)
- Animal Form and Functions (38)
- Animal Physiology (65)
- Biochemistry (33)
- Biophysics (25)
- Biotechnology (52)
- Botany (42)
- Plant morphology (6)
- Plant Physiology (26)
- Cell Biology (107)
- Cell Cycle (14)
- Cell Signaling (21)
- Chemistry (9)
- Developmental Biology (36)
- Fertilization (13)
- Ecology (5)
- Embryology (17)
- Endocrinology (10)
- Environmental biology (3)
- Genetics (59)
- DNA (27)
- Inheritance (13)
- Histology (3)
- Hormone (3)
- Immunology (29)
- life science (76)
- Material science (8)
- Microbiology (18)
- Virus (8)
- Microscopy (18)
- Molecular Biology (113)
- parasitology (6)
- Physics (3)
- Physiology (11)
- Plant biology (26)
- Uncategorized (7)
- Zoology (112)
- Classification (6)
- Invertebrate (7)




