-
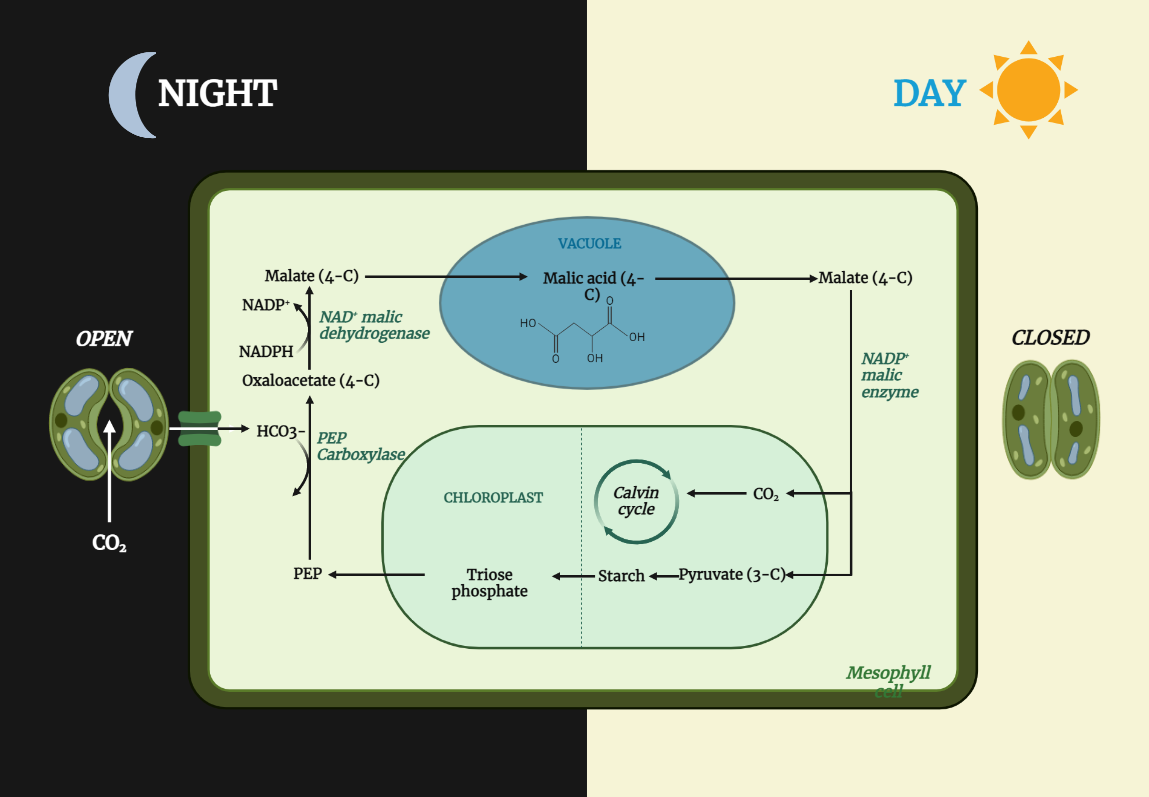
CAM plants
CAM (Crassulacean Acid Metabolism) plants have evolved a specialized carbon fixation pathway that allows them to carry out photosynthesis while minimizing water loss, making them well adapted to arid and semi-arid environments. Their ability to store water in their leaves, stems, and roots, along with their thick, waxy leaves and shallow root system, helps them…
-

CAM Pathway
The CAM pathway is a unique mechanism for carbon fixation in plants that allows them to carry out photosynthesis in arid environments with minimal water loss. By fixing carbon dioxide at night and storing it as malic acid, CAM plants are able to use it during the day to carry out photosynthesis without losing water.…
-
C4 Plants
C4 plants have evolved a unique mechanism for carbon fixation that allows them to efficiently produce glucose in hot and dry environments. This mechanism, known as the C4 pathway, involves the spatial separation of carbon dioxide fixation and the Calvin cycle. The C4 pathway provides several ecological advantages to plants, including increased water use efficiency…
-
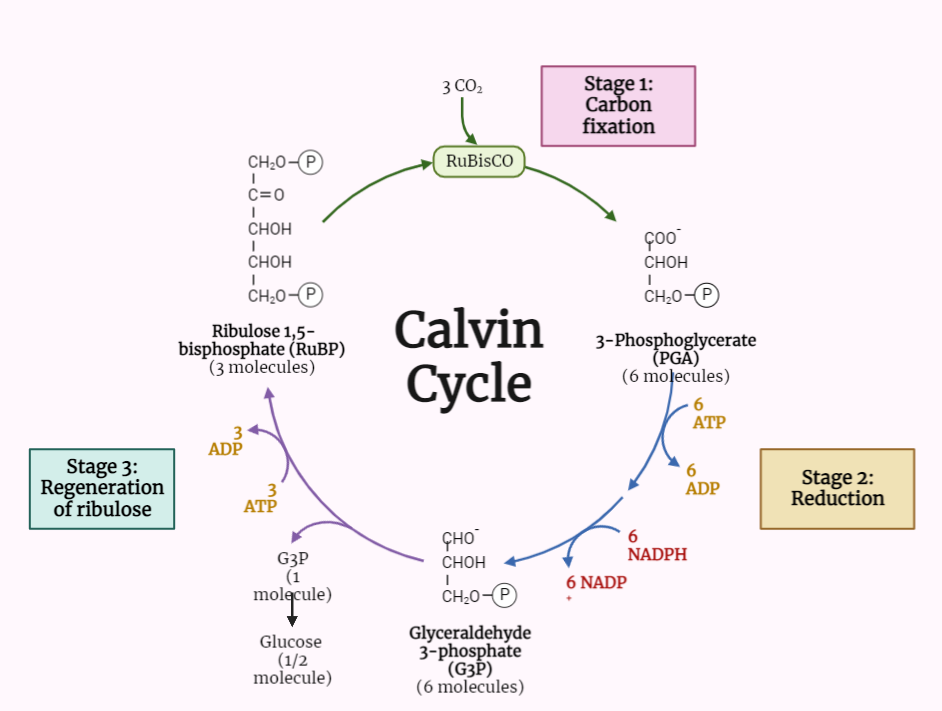
Calvin-Benson Cycle
The Calvin-Benson cycle is a fundamental process in photosynthesis, the metabolic pathway by which autotrophs, such as plants, algae, and some bacteria, convert light energy into chemical energy in the form of glucose. This cycle takes place in the chloroplasts of these organisms and is responsible for fixing carbon dioxide (CO2) from the atmosphere into…
Categories
- Anatomy (9)
- Animal Form and Functions (38)
- Animal Physiology (65)
- Biochemistry (33)
- Biophysics (25)
- Biotechnology (52)
- Botany (42)
- Plant morphology (6)
- Plant Physiology (26)
- Cell Biology (107)
- Cell Cycle (14)
- Cell Signaling (21)
- Chemistry (9)
- Developmental Biology (36)
- Fertilization (13)
- Ecology (5)
- Embryology (17)
- Endocrinology (10)
- Environmental biology (3)
- Genetics (59)
- DNA (27)
- Inheritance (13)
- Histology (3)
- Hormone (3)
- Immunology (29)
- life science (76)
- Material science (8)
- Microbiology (18)
- Virus (8)
- Microscopy (18)
- Molecular Biology (113)
- parasitology (6)
- Physics (3)
- Physiology (11)
- Plant biology (26)
- Uncategorized (7)
- Zoology (112)
- Classification (6)
- Invertebrate (7)




