-
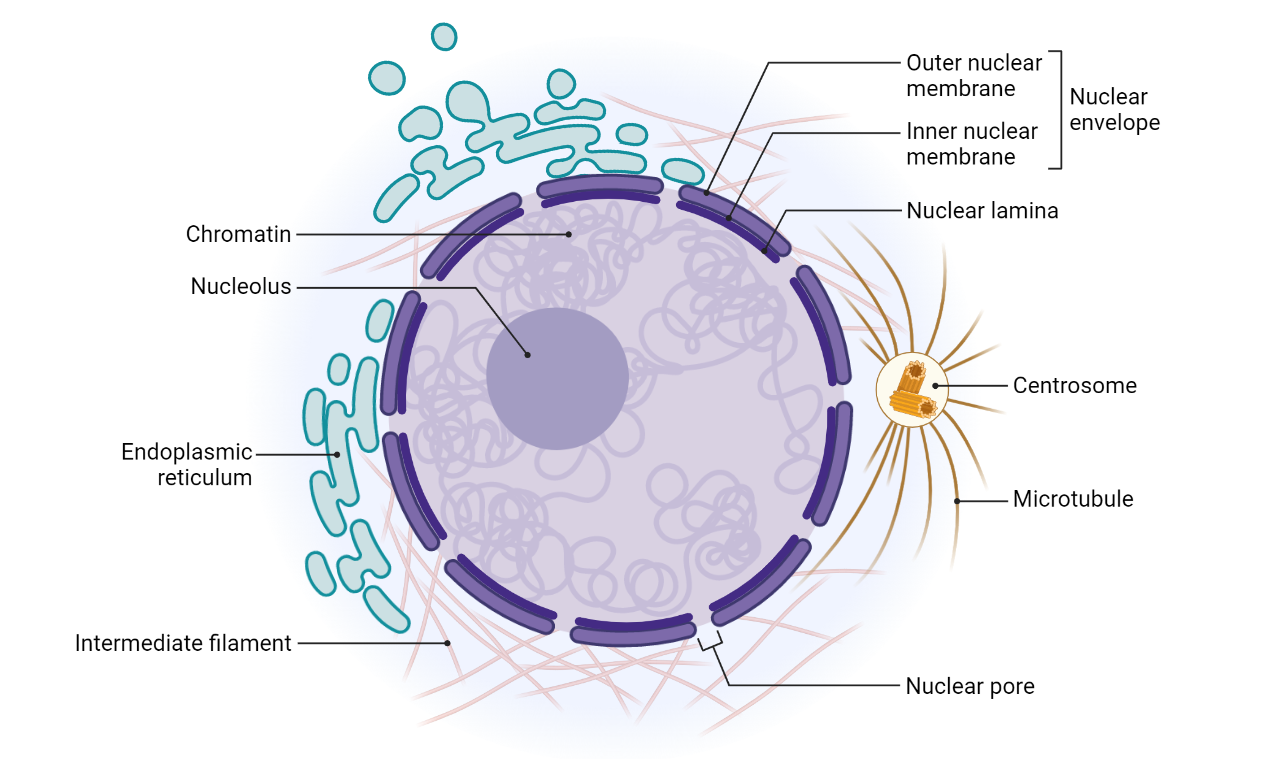
Nucleus – Ultra structure
The nucleus is a vital organelle found in eukaryotic cells, which contains the genetic material of the cell in the form of DNA. It plays a significant role in the regulation of cell growth, division, and gene expression. The ultrastructure of the nucleus includes the nuclear envelope, nucleoplasm, and chromatin. The nuclear envelope surrounds the…
-
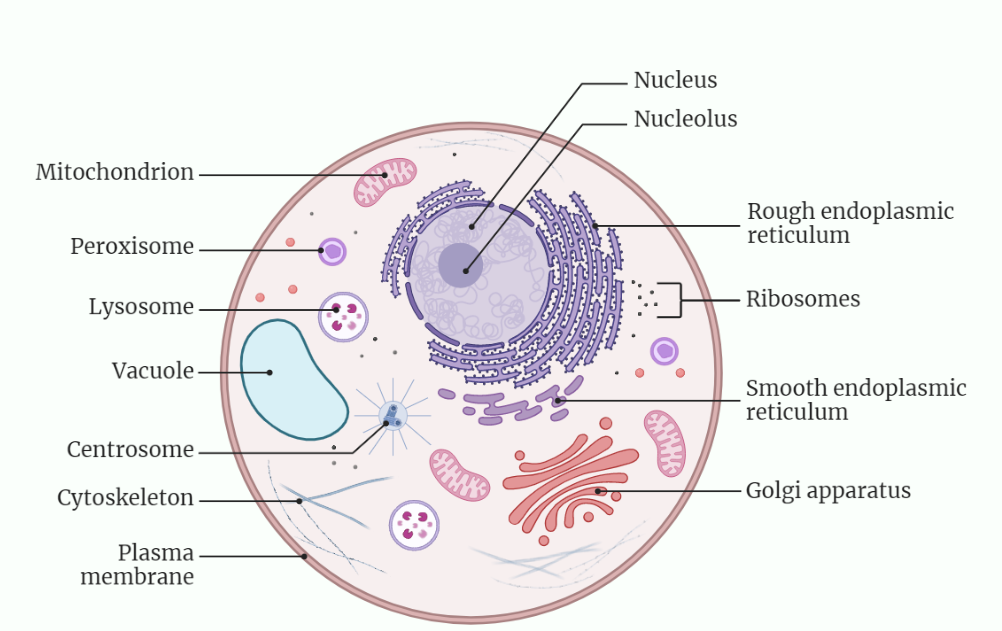
Cellular Compartmentalization
Cellular compartmentalization is a fundamental process that allows eukaryotic cells to carry out different functions simultaneously and create specialized environments within the cell. The different compartments within the cell have specific functions and contain specific proteins and other molecules. Dysfunction in cellular compartmentalization can lead to various diseases, highlighting the importance of this process in…
-
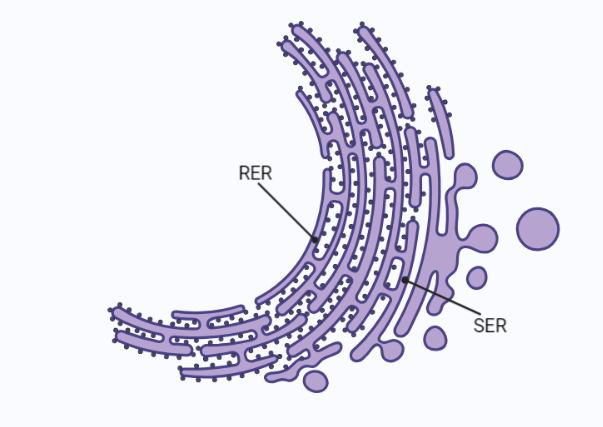
Endoplasmic Reticulum
The Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER) is a vital organelle in eukaryotic cells, playing multiple crucial roles. From protein synthesis, folding, and modification to lipid metabolism and calcium storage, the ER ensures the cell’s proper functioning. The Rough ER, adorned with ribosomes, synthesizes proteins, while the Smooth ER is responsible for lipid synthesis and detoxification. Additionally, the…
Categories
- Anatomy (9)
- Animal Form and Functions (38)
- Animal Physiology (65)
- Biochemistry (33)
- Biophysics (25)
- Biotechnology (52)
- Botany (42)
- Plant morphology (6)
- Plant Physiology (26)
- Cell Biology (107)
- Cell Cycle (14)
- Cell Signaling (21)
- Chemistry (9)
- Developmental Biology (36)
- Fertilization (13)
- Ecology (5)
- Embryology (17)
- Endocrinology (10)
- Environmental biology (3)
- Genetics (59)
- DNA (27)
- Inheritance (13)
- Histology (3)
- Hormone (3)
- Immunology (29)
- life science (76)
- Material science (8)
- Microbiology (18)
- Virus (8)
- Microscopy (18)
- Molecular Biology (113)
- parasitology (6)
- Physics (3)
- Physiology (11)
- Plant biology (26)
- Uncategorized (7)
- Zoology (112)
- Classification (6)
- Invertebrate (7)




