-

Peroxisome: Structure and Function
Peroxisomes are small, spherical organelles found in eukaryotic cells that play a crucial role in cellular metabolism. They are enclosed by a single membrane and contain enzymes responsible for specific metabolic reactions, such as the metabolism of lipids and the detoxification of harmful substances. Peroxisomes are distinct from lysosomes, as they do not degrade macromolecules.…
-
Centrosomes Structure and Function
Centrosomes are vital organelles in eukaryotic cells that play an essential role in the organization of the cell’s microtubule cytoskeleton and the proper distribution of genetic material during cell division. Composed of two cylindrical centrioles surrounded by pericentriolar material, these organelles act as nucleation sites for the formation of microtubules, which are crucial for cell…
-
The Golgi Apparatus: Structure and Function
The Golgi apparatus, a crucial organelle in eukaryotic cells, plays a vital role in processing, sorting, and transporting proteins and lipids. Comprising stacked cisternae with distinct regions, it employs a myriad of enzymes for modifications. This dynamic structure ensures proper cellular function by facilitating the formation of lysosomes, secretory vesicles, and the extracellular matrix. Understanding…
-
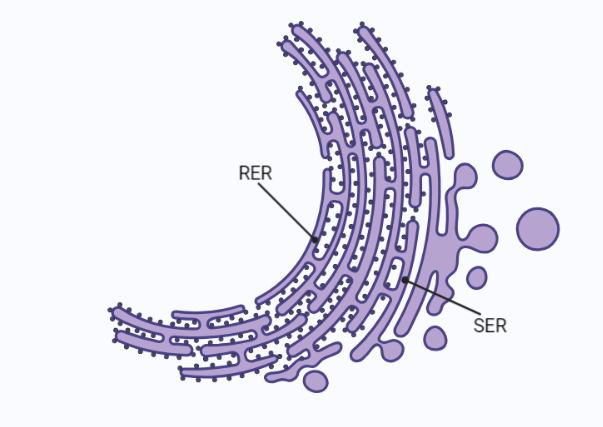
Endoplasmic Reticulum
The Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER) is a vital organelle in eukaryotic cells, playing multiple crucial roles. From protein synthesis, folding, and modification to lipid metabolism and calcium storage, the ER ensures the cell’s proper functioning. The Rough ER, adorned with ribosomes, synthesizes proteins, while the Smooth ER is responsible for lipid synthesis and detoxification. Additionally, the…
-
Lysozomes
Lysozomes, the essential organelles in eukaryotic cells, play a pivotal role in cellular material degradation. Enclosed within a lipid bilayer, these spherical structures house hydrolytic enzymes responsible for breaking down bacteria, old organelles, and other cellular components. Additionally, lysozomes contribute to autophagy, cellular protection against harmful agents, and lipid metabolism. Formation from the Golgi apparatus…
-
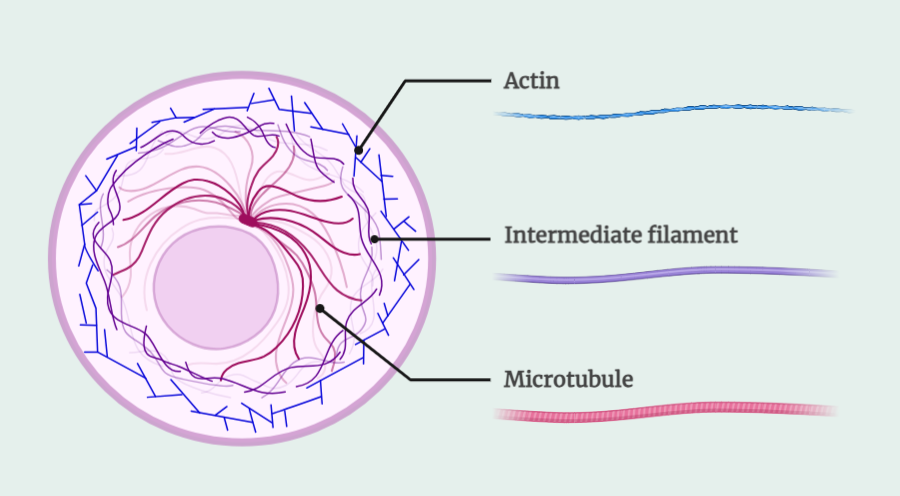
The cytoskeleton
The cytoskeleton, a complex network of protein filaments, serves as the architectural backbone of eukaryotic cells. Comprised of microfilaments, intermediate filaments, and microtubules, it provides structural support, cell shape, and motility. Functionally versatile, the cytoskeleton plays crucial roles in cell division, endocytosis, and exocytosis. Regulated by specific proteins, its dynamic nature underlies various cellular processes.…
Categories
- Anatomy (9)
- Animal Form and Functions (36)
- Animal Physiology (62)
- Biochemistry (32)
- Biophysics (15)
- Biotechnology (43)
- Botany (41)
- Plant morphology (6)
- Plant Physiology (26)
- Cell Biology (106)
- Cell Cycle (14)
- Cell Signaling (20)
- Chemistry (9)
- Developmental Biology (29)
- Fertilization (9)
- Ecology (5)
- Embryology (11)
- Endocrinology (10)
- Environmental biology (3)
- Genetics (58)
- DNA (26)
- Inheritance (12)
- Histology (3)
- Hormone (3)
- Immunology (29)
- life science (70)
- Material science (8)
- Microbiology (18)
- Virus (8)
- Microscopy (8)
- Molecular Biology (110)
- parasitology (6)
- Physics (3)
- Physiology (11)
- Plant biology (25)
- Uncategorized (7)
- Zoology (108)
- Classification (6)
- Invertebrate (7)



