-
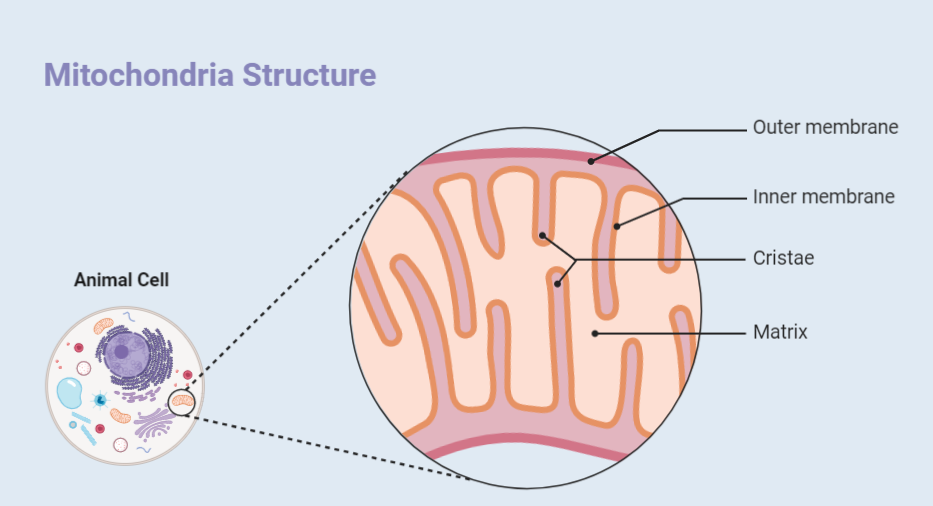
Mitochondria
Mitochondria are organelles found in eukaryotic cells responsible for generating energy in the form of adenosine triphosphate (ATP). Due to their essential role in cellular respiration, they are often referred to as the powerhouses of the cell. Mitochondria have a unique structure consisting of an outer membrane, intermembrane space, inner membrane, cristae, and matrix. They…
-
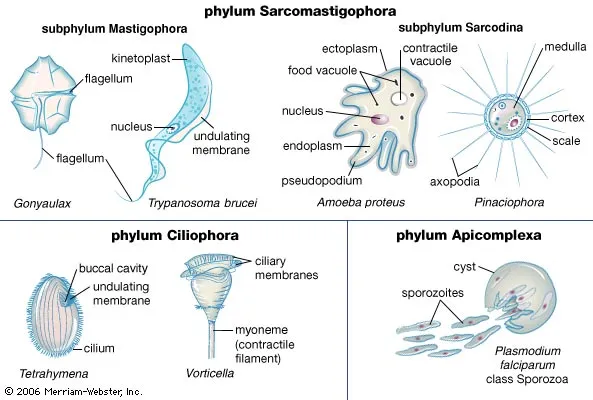
Classification of Protozoa (According to Levine et. al., 1980)
Introduction General Characteristics of Protozoa Classification of Protozoa Phylum Sarcomastigophora Phylum Mastigophora Phylum Opalinata Phylum Ciliophora Phylum Apicomplexa Phylum Microspora and Myxozoa Phylum Acanthamoeba Conclusion
-
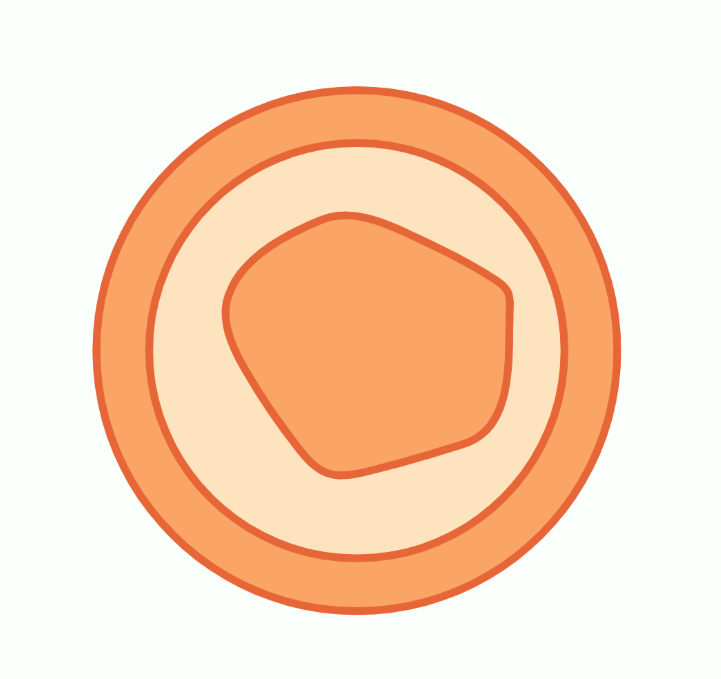

Peroxisome: Structure and Function
Peroxisomes are small, spherical organelles found in eukaryotic cells that play a crucial role in cellular metabolism. They are enclosed by a single membrane and contain enzymes responsible for specific metabolic reactions, such as the metabolism of lipids and the detoxification of harmful substances. Peroxisomes are distinct from lysosomes, as they do not degrade macromolecules.…
-
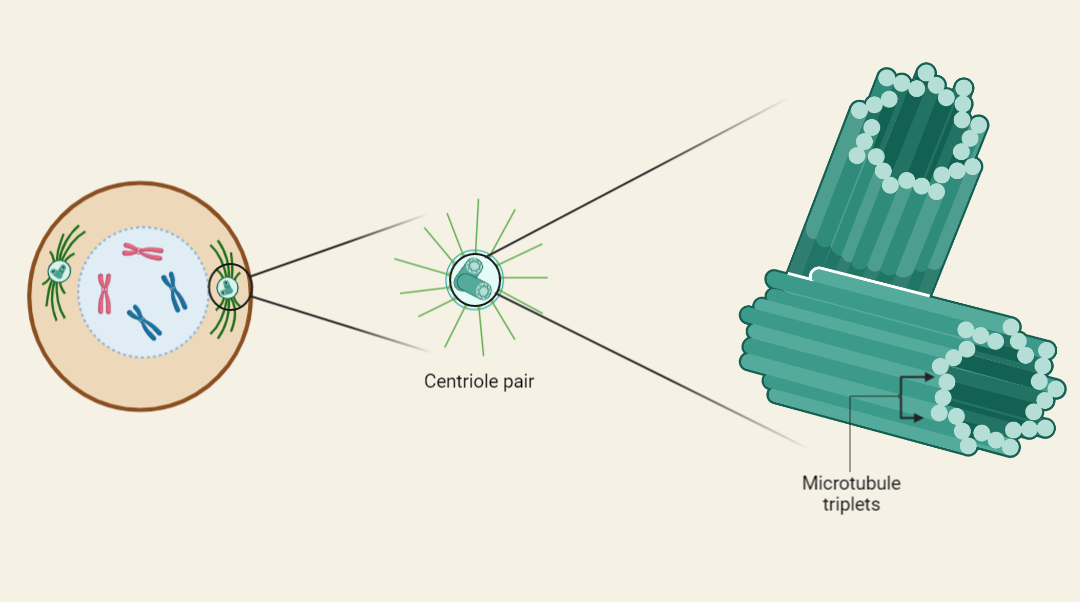
Centrosomes Structure and Function
Centrosomes are vital organelles in eukaryotic cells that play an essential role in the organization of the cell’s microtubule cytoskeleton and the proper distribution of genetic material during cell division. Composed of two cylindrical centrioles surrounded by pericentriolar material, these organelles act as nucleation sites for the formation of microtubules, which are crucial for cell…
-
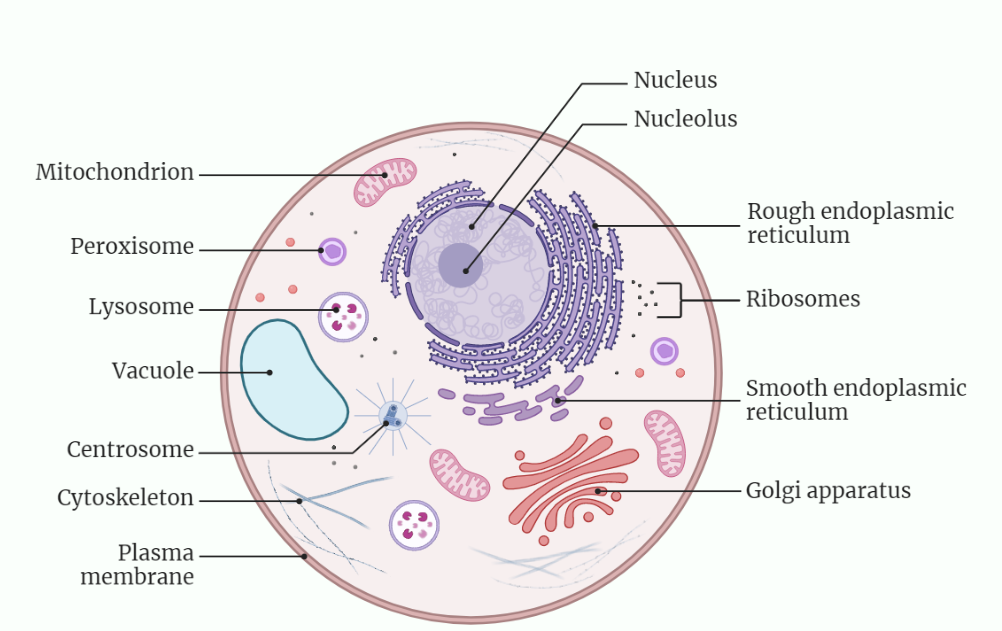
Cellular Compartmentalization
Cellular compartmentalization is a fundamental process that allows eukaryotic cells to carry out different functions simultaneously and create specialized environments within the cell. The different compartments within the cell have specific functions and contain specific proteins and other molecules. Dysfunction in cellular compartmentalization can lead to various diseases, highlighting the importance of this process in…
-
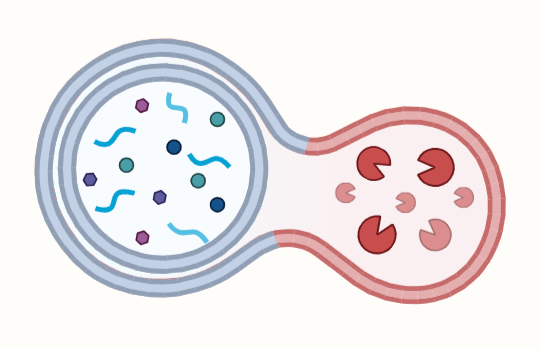
Lysozomes
Lysozomes, the essential organelles in eukaryotic cells, play a pivotal role in cellular material degradation. Enclosed within a lipid bilayer, these spherical structures house hydrolytic enzymes responsible for breaking down bacteria, old organelles, and other cellular components. Additionally, lysozomes contribute to autophagy, cellular protection against harmful agents, and lipid metabolism. Formation from the Golgi apparatus…
-
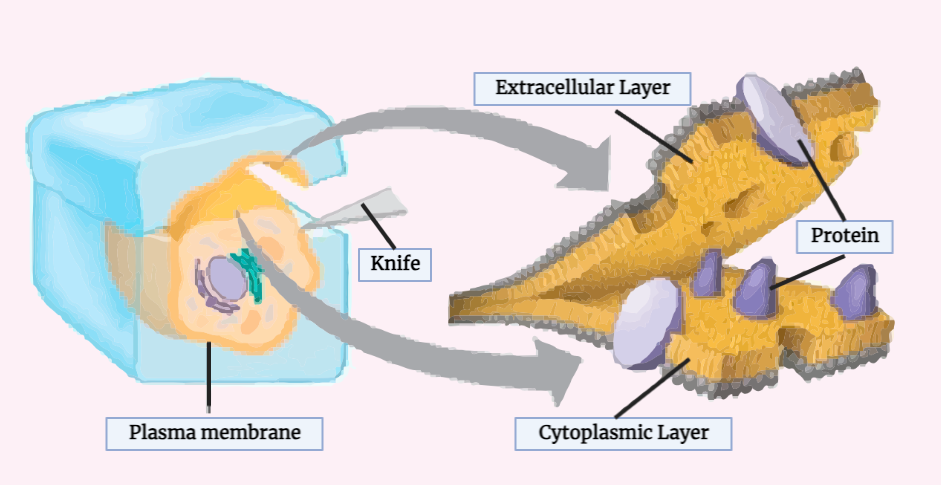
Freeze Fracture Technique
The Freeze Fracture Technique is a powerful method utilized in the study of cell biology and other biological samples. By freezing and breaking a sample, its internal structure is revealed and can be examined under an electron microscope. This technique is commonly applied to investigate cell membranes, organelles, microorganisms, as well as in fields like…
Categories
- Anatomy (9)
- Animal Form and Functions (38)
- Animal Physiology (65)
- Biochemistry (33)
- Biophysics (25)
- Biotechnology (52)
- Botany (42)
- Plant morphology (6)
- Plant Physiology (26)
- Cell Biology (107)
- Cell Cycle (14)
- Cell Signaling (21)
- Chemistry (9)
- Developmental Biology (36)
- Fertilization (13)
- Ecology (5)
- Embryology (17)
- Endocrinology (10)
- Environmental biology (3)
- Genetics (59)
- DNA (27)
- Inheritance (13)
- Histology (3)
- Hormone (3)
- Immunology (29)
- life science (76)
- Material science (8)
- Microbiology (18)
- Virus (8)
- Microscopy (18)
- Molecular Biology (113)
- parasitology (6)
- Physics (3)
- Physiology (11)
- Plant biology (26)
- Uncategorized (7)
- Zoology (112)
- Classification (6)
- Invertebrate (7)




