-
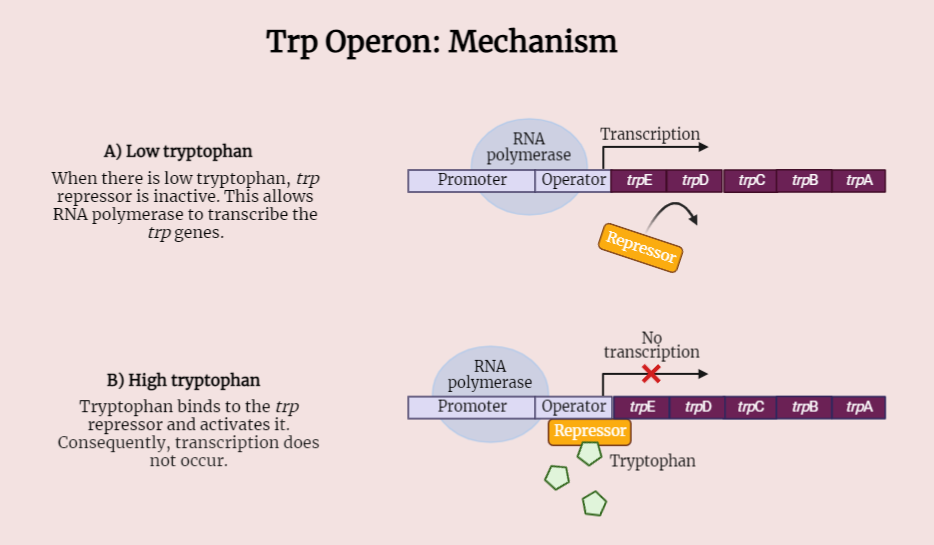
Attenuation in TRP Operon
Attenuation is a sophisticated gene regulation mechanism found in the TRP operon, responsible for tryptophan synthesis in bacteria. By utilizing the leader peptide and tryptophan as key players, attenuation allows precise control of gene expression based on tryptophan levels. The leader peptide acts as a sensor, adjusting the secondary structure to either block or allow…
-
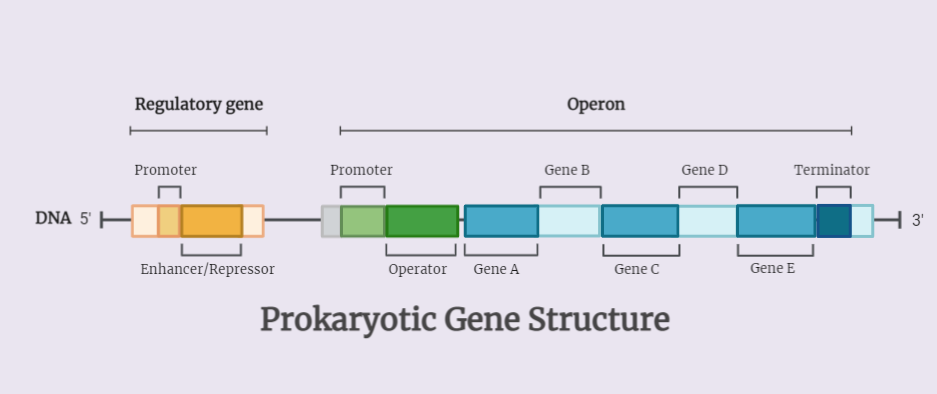
Trp Operon
The Trp operon is a genetic regulatory system in bacteria that controls the production of enzymes for tryptophan synthesis. It consists of a promoter, operator, and structural gene region. Induction and repression mechanisms regulate transcription based on tryptophan levels. Feedback inhibition further modulates the operon. Understanding the Trp operon sheds light on genetic regulation, cell…
-
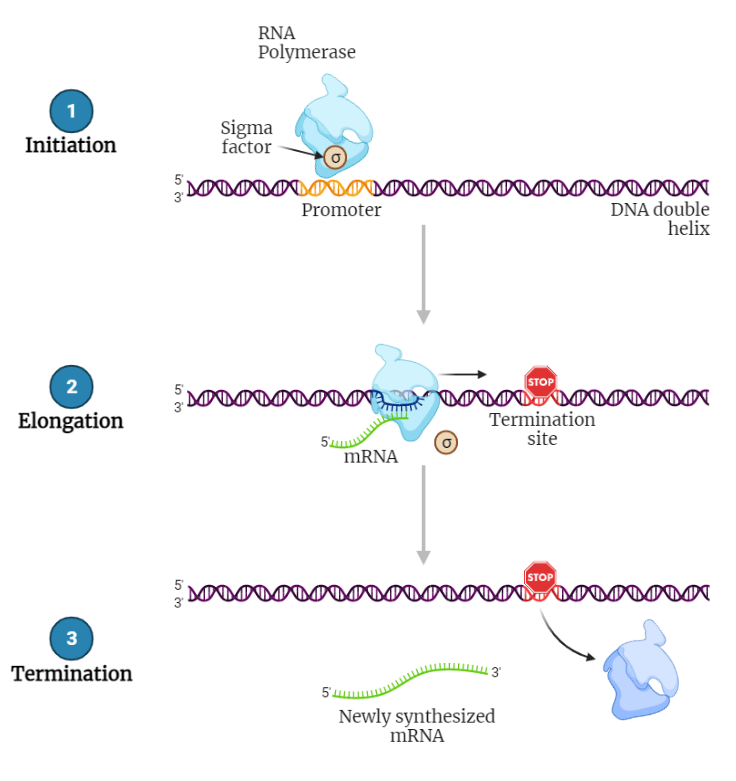
Prokaryotic Transcription
Introduction: Promoter recognition and binding: Initiation: Elongation: Termination: In summary, Prokaryotic transcription is the process of converting genetic information from DNA to RNA. This process is mediated by the enzyme RNA polymerase. The process includes promoter recognition and binding, initiation, elongation, and termination. The RNA polymerase recognizes the promoter by the help of sigma factor…
Categories
- Anatomy (9)
- Animal Form and Functions (38)
- Animal Physiology (65)
- Biochemistry (33)
- Biophysics (25)
- Biotechnology (52)
- Botany (42)
- Plant morphology (6)
- Plant Physiology (26)
- Cell Biology (107)
- Cell Cycle (14)
- Cell Signaling (21)
- Chemistry (9)
- Developmental Biology (36)
- Fertilization (13)
- Ecology (5)
- Embryology (17)
- Endocrinology (10)
- Environmental biology (3)
- Genetics (59)
- DNA (27)
- Inheritance (13)
- Histology (3)
- Hormone (3)
- Immunology (29)
- life science (76)
- Material science (8)
- Microbiology (18)
- Virus (8)
- Microscopy (18)
- Molecular Biology (113)
- parasitology (6)
- Physics (3)
- Physiology (11)
- Plant biology (26)
- Uncategorized (7)
- Zoology (112)
- Classification (6)
- Invertebrate (7)




