Table of Contents
Introduction
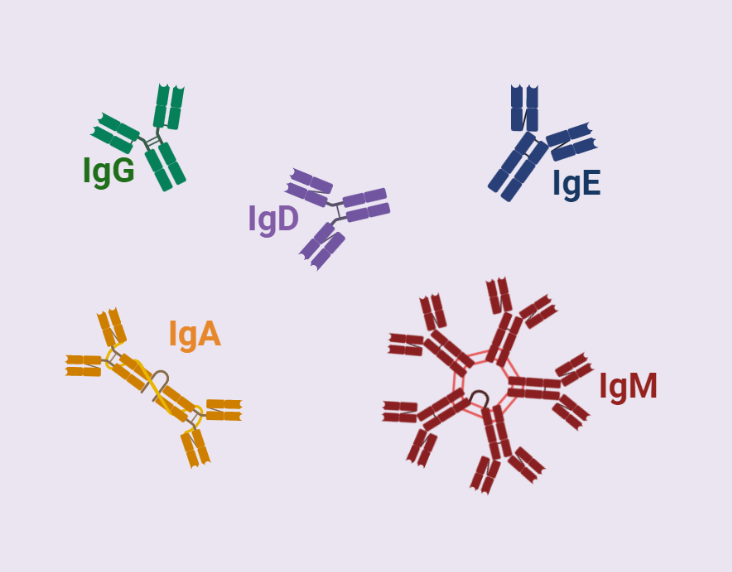
Antibodies, also known as immunoglobulins, are a class of proteins that play a critical role in the immune response. They are produced by B-lymphocytes and are able to specifically bind to a wide variety of antigens. There are five main types antibodies present based on their constant domains, each with distinct properties and functions.
Types of antibodies
There are 5 main types of antibodies present :
I. IgG
- IgG is the most common class of antibody in the bloodstream, comprising about 75% of the total immunoglobulin.
- IgG is produced in secondary immune response and provides long-term protection against pathogens.
- IgG can cross the placenta and provide passive immunity to the fetus.
- IgG can activate the complement system, which helps to kill pathogens, and can also act as an opsonin, which helps to mark pathogens for phagocytosis.
II. IgM
- IgM is the first class of antibody to be produced in response to an antigen and is found in the bloodstream, lymph, and tissue fluids.
- IgM is a pentamer, composed of five IgM monomers joined together by a J-chain.
- IgM can activate the complement system, which helps to kill pathogens, and can also act as an opsonin, which helps to mark pathogens for phagocytosis.
- IgM is the most effective class of antibody at neutralizing viruses, due to its large size and ability to bind to multiple epitopes.
III. IgA
- IgA is the second most common class of antibody in the bloodstream, and is also found in secretions such as saliva, tears, and mucus.
- IgA is present in the gut and respiratory tracts, where it helps to protect against infection.
- IgA can also act as an opsonin, which helps to mark pathogens for phagocytosis.
- IgA is able to dimerize, forming a secretory IgA (sIgA) that can protect against pathogens in secretions and on mucosal surfaces.
IV. IgD
- IgD is present on the surface of B-lymphocytes and is thought to play a role in the activation of these cells.
- IgD is found in low levels in the bloodstream and is not known to play a direct role in immunity.
V. IgE
- IgE is present in low levels in the bloodstream and is involved in the immune response to parasites and in allergic reactions.
- IgE binds to Fc receptors on the surface of mast cells and basophils, leading to the release of inflammatory mediators.
Conclusion
- Antibodies are a class of proteins that play a critical role in the immune response.
- Antibodies are divided into five main classes based on their constant domains, each with distinct properties and functions.
- IgG, IgM, IgA, IgD and IgE are five classes of antibodies with distinct properties and functions.
- IgG is the most common class of antibody in the bloodstream, IgM is the first class of antibody to be produced in response to an antigen and is found in the bloodstream, lymph, and tissue fluids and so on.